Understanding Triceps Tendonitis
Triceps tendonitis is a painful condition that affects the triceps tendon, a thick band of tissue connecting the triceps muscle to the elbow. It is characterized by inflammation, irritation, or damage to this tendon. This condition typically arises due to overuse, repetitive motions, or sudden increases in physical activity.
1. Causes of Triceps Tendonitis
Triceps tendonitis can develop for various reasons, with the primary cause being overuse or repetitive stress on the triceps tendon. Some common contributing factors include:
- Excessive Weightlifting: Engaging in heavy weightlifting or lifting weights with improper form can strain the triceps tendon.
- Sports and Athletics: Athletes involved in activities like weightlifting, baseball, tennis, and golf are at a higher risk due to repetitive arm movements.
- Age and Degeneration: As we age, tendons may naturally weaken and become more susceptible to injury.
- Sudden Increase in Activity: Rapidly increasing the intensity or duration of physical activity can lead to tendonitis.
- Previous Injuries: Prior elbow or triceps injuries may predispose individuals to triceps tendonitis.
1.1 Common Symptoms of Triceps Tendonitis
Triceps tendonitis presents several noticeable symptoms, including:
- Pain: Individuals with triceps tendonitis often experience pain at the back of the elbow, which can range from mild to severe.
- Swelling: Swelling around the elbow joint may occur due to inflammation.
- Tenderness: The area around the triceps tendon becomes tender to the touch.
- Reduced Range of Motion: Triceps tendonitis can limit the ability to fully extend the elbow or perform certain movements.
- Weakness: Some people notice a decrease in triceps strength, affecting everyday activities.
1.2 Impact on Daily Life
Triceps tendonitis can significantly impact daily life, especially if left untreated. Simple tasks like lifting objects, carrying groceries, or even typing on a keyboard may become painful and challenging. Understanding the condition’s effects is crucial for seeking appropriate treatment and relief.
This section provides a foundational understanding of triceps tendonitis, including its definition, causes, common symptoms, and its impact on daily life. In the following sections, we will delve deeper into its diagnosis and various treatment options, including the use of braces to manage the condition effectively.
2. Diagnosis and Medical Evaluation
- Importance of Seeking Professional Diagnosis
- To accurately diagnose triceps tendonitis, it is crucial to consult a healthcare professional or orthopedic specialist. Self-diagnosis can lead to misunderstandings and potentially delay effective treatment.
- Physical Examination
- During the diagnostic process, the healthcare provider will conduct a physical examination of the affected elbow. They will assess for tenderness, swelling, range of motion, and signs of inflammation.
- Imaging Studies
- In some cases, diagnostic imaging studies like X-rays or ultrasound may be ordered. These tests can help visualize the triceps tendon and rule out other potential issues such as fractures or tears.
- Discussion of Symptoms and Medical History
- The healthcare provider will discuss your symptoms in detail and inquire about your medical history. Any previous injuries or activities that may have contributed to triceps tendonitis will be considered.
- Confirming the Diagnosis
- Based on the physical examination, imaging results, and medical history, the healthcare provider will confirm whether you have triceps tendonitis. A clear diagnosis is essential for developing an effective treatment plan.
By seeking professional diagnosis and undergoing a thorough evaluation, individuals with triceps tendonitis can receive proper medical guidance and tailored treatment options. This ensures that the condition is accurately identified, leading to more effective management and recovery.
3. Conservative Treatments for Triceps Tendonitis
Triceps tendonitis can often be effectively managed through conservative treatments. These methods aim to alleviate pain, reduce inflammation, and promote healing. Here’s a table summarizing common conservative treatments:
| Treatment Option | Description |
| Rest | Giving the affected triceps tendon time to heal is crucial. |
| Ice | Applying ice to the affected area can help reduce swelling. |
| Compression | Compression sleeves or bandages can provide support. |
| Elevation | Elevating the affected arm can minimize swelling. |
| Physical Therapy | Targeted exercises and stretches can improve strength. |
| Anti-Inflammatory | Over-the-counter medications may reduce inflammation. |
| Modified Activities | Avoid activities that exacerbate the condition. |
Conservative treatments are often the first line of defense against triceps tendonitis. They are non-invasive and can effectively relieve symptoms, allowing individuals to resume their regular activities with less pain and discomfort.
4. Role of Bracing in Triceps Tendonitis
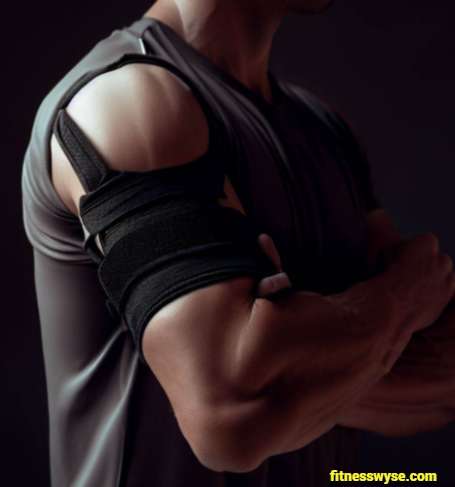

Braces play a significant role in managing triceps tendonitis by providing support and stability to the affected area. Here, we’ll explore the benefits of using braces and how they can aid in the treatment process.
4.1. Stability and Support
Braces for triceps tendonitis are designed to stabilize the elbow joint and the triceps tendon. They provide external support, reducing strain on the tendon during daily activities or exercise.
4.2. Pain Reduction
One of the primary benefits of using a triceps tendonitis brace is pain reduction. By limiting excessive movement and providing compression, braces help alleviate pain and discomfort associated with the condition.
4.3. Inflammation Control
Braces can help control inflammation by applying gentle pressure to the affected area. This can reduce swelling and promote the healing process.
4.4. Improved Range of Motion
Some braces are designed to offer controlled motion, allowing for gradual improvements in the range of motion. This can be particularly beneficial during the recovery phase.
4.5. Posture Correction
Proper posture can play a role in triceps tendonitis management. Certain braces provide posture correction, ensuring that the affected arm is positioned optimally for healing.
4.6. Customization
Braces come in various types and sizes to suit individual needs. Whether you require a specific range of motion or additional compression, there’s likely a brace that fits your requirements.
4.7. Complementing Other Treatments
Bracing can complement other conservative treatments like rest, physical therapy, and anti-inflammatory medications. It provides an additional layer of support to the overall treatment plan.
4.8. Consultation with a Healthcare Provider
It’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider or orthopedic specialist before using a triceps tendonitis brace. They can recommend the most suitable type of brace and provide guidance on its usage.
Using a brace as part of the treatment plan can enhance the management of triceps tendonitis, offering relief from pain and supporting the healing process. However, the specific type and usage of the brace should be determined in consultation with a healthcare professional.
5. Choosing the Right Triceps Tendonitis Brace
Selecting the appropriate triceps tendonitis brace is crucial for effective management. Here, we’ll discuss the factors to consider when choosing the right brace for your needs.
5.1. Type of Brace
There are various types of braces available for triceps tendonitis, including elbow sleeves, straps, and full-arm braces. Determine which type aligns with your comfort and treatment requirements.
5.2. Fit and Sizing
Ensuring that the brace fits properly is essential. Measure your arm accurately and refer to sizing guidelines to select the right size. A well-fitted brace offers better support.
5.3. Level of Support
Consider the level of support needed. Some individuals may require strong compression and stability, while others may benefit from a lighter, more flexible brace.
5.4. Range of Motion
Evaluate your range of motion requirements. Some braces restrict motion to promote healing, while others allow controlled movement. Choose according to your healthcare provider’s recommendations.
5.5. Comfort and Material
Look for a brace made from comfortable, breathable materials. It should be wearable for extended periods without causing discomfort or skin irritation.
5.6. Durability
Check the durability of the brace. A well-constructed brace can provide long-lasting support throughout your recovery process.
5.7. Ease of Use
Consider how easy it is to put on and take off the brace. Some individuals may require assistance, while others prefer a user-friendly design.
5.8. Healthcare Provider’s Recommendation
Always consult with your healthcare provider or orthopedic specialist for their recommendation. They can assess your condition and provide guidance on the most suitable brace for your specific needs.
Choosing the right triceps tendonitis brace involves careful consideration of your individual requirements, comfort, and the level of support needed. Consulting with a healthcare professional ensures that you make an informed choice to aid in your recovery process.
read more : TRICEP REPAIR PROTOCOL
6. Using a Triceps Tendonitis Brace

Using a triceps tendonitis brace effectively is crucial to maximize its benefits and aid in the healing process. Here, we’ll provide instructions on how to properly wear and adjust the brace for optimal support.
6.1. Putting on the Brace
Follow these steps to put on your triceps tendonitis brace:
- Ensure Cleanliness: Start with clean and dry skin to prevent irritation.
- Position the Brace: Place the brace over your affected triceps tendon area, ensuring it covers the target region.
- Adjust Straps: Secure any straps, buckles, or closures to keep the brace in place.
- Comfortable Fit: Adjust the tightness to a comfortable but supportive level. It should provide compression without being too restrictive.
6.2. Daily Wear
Wear the brace as directed by your healthcare provider or orthopedic specialist. It may be recommended for specific activities or throughout the day, depending on your condition.
6.3. Maintenance and Care
To maintain the brace’s effectiveness and hygiene, follow these guidelines:
- Regular Cleaning: Clean the brace according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
- Inspect for Wear: Check the brace for signs of wear and tear and replace it if necessary.
- Skin Care: Pay attention to your skin beneath the brace to prevent any irritation or discomfort.
6.4. Consultation with a Healthcare Provider
If you experience any discomfort or if the brace doesn’t seem to be providing the expected support, consult your healthcare provider promptly. They can adjust the fit or recommend alternative solutions.
6.5. Duration of Use
Follow your healthcare provider’s recommendations regarding the duration of brace use. They will provide guidance on when it’s safe to gradually reduce or discontinue using the brace as your condition improves.
Using a triceps tendonitis brace correctly is essential for its effectiveness in managing the condition. Proper positioning, fit, and care ensure that you receive the maximum benefit from the brace during your recovery process.
7. Combining Bracing with Other Treatment Approaches
Effectively managing triceps tendonitis often involves a multi-faceted approach. Bracing can be a valuable component of this strategy when combined with other conservative treatments. Here, we’ll explore how bracing complements other treatment approaches:
7.1. Rest and Immobilization
- Brace Support: A triceps tendonitis brace helps immobilize and support the affected area, allowing the tendon to rest and heal.
7.2. Physical Therapy
- Enhanced Therapy: Bracing can be used in conjunction with physical therapy exercises to maximize the benefits of both approaches.
- Controlled Motion: Some braces offer controlled motion, facilitating specific therapeutic exercises.
7.3. Medications
- Reduced Pain: Bracing can contribute to pain reduction, potentially reducing the need for pain medications.
- Anti-Inflammatory: By controlling inflammation, braces may complement the action of anti-inflammatory medications.
7.4. Lifestyle Modifications
- Activity Support: Braces offer support during daily activities, minimizing strain on the triceps tendon.
- Posture Correction: Certain braces promote proper posture, preventing exacerbation of the condition.
7.5. Healthcare Provider’s Guidance
- Treatment Coordination: Consult with your healthcare provider to ensure that bracing aligns with your overall treatment plan.
- Adjustments: They can make necessary adjustments to your treatment regimen as needed.
Combining bracing with other treatment approaches creates a comprehensive strategy for managing triceps tendonitis. It can enhance the effectiveness of rest, therapy, medications, and lifestyle modifications, ultimately contributing to a more successful recovery. Always consult with your healthcare provider for personalized guidance on combining treatments.
8. Tips for Effective Triceps Tendonitis Management
Managing triceps tendonitis effectively involves not only the use of braces and other treatments but also lifestyle adjustments and self-care. Here are some valuable tips to aid in the management of triceps tendonitis:
8.1. Follow Medical Advice
- Listen to Professionals: Adhere to the guidance provided by your healthcare provider or orthopedic specialist regarding treatment, brace usage, and exercise.
8.2. Prioritize Rest
- Give It Time: Allow your triceps tendon to rest and heal. Avoid activities that aggravate the condition.
8.3. Warm-Up and Stretch
- Pre-Activity Routine: Before engaging in physical activities, warm up and perform gentle stretches to prepare your muscles and tendons.
8.4. Maintain Proper Posture
- Ergonomic Considerations: Ensure that your workspace and daily activities promote good posture to minimize strain on the triceps tendon.
8.5. Gradual Return to Activity
- Don’t Rush: As your condition improves, slowly reintroduce activities and exercises under the guidance of your healthcare provider.
8.6. Stay Hydrated
- Hydration Matters: Proper hydration supports tendon health. Drink an adequate amount of water daily.
8.7. Balanced Diet
- Nutrition Matters: Consume a balanced diet rich in nutrients that support tendon health, such as collagen.
8.8. Brace Maintenance
- Care and Cleanliness: Regularly clean and maintain your triceps tendonitis brace according to manufacturer instructions.
8.9. Monitor for Improvement
- Track Progress: Keep a record of your symptoms and discuss improvements or setbacks with your healthcare provider.
8.10. Patience and Consistency
- Healing Takes Time: Understand that tendon healing can be a gradual process. Consistency in following treatment recommendations is key.
By incorporating these tips into your daily routine and treatment plan, you can enhance the management of triceps tendonitis. Remember that it’s essential to consult with your healthcare provider for personalized advice and adjustments along the way.
9. When to Seek Medical Attention for Triceps Tendonitis
Recognizing when to seek medical attention is crucial for individuals dealing with triceps tendonitis. Here, we’ll discuss the signs and situations that warrant a visit to a healthcare provider:
9.1. Persistent Pain
- If you experience persistent or worsening pain in your triceps that doesn’t improve with rest and conservative treatments, consult a healthcare professional.
9.2. Limited Range of Motion
- Difficulty in moving your elbow or extending your arm fully could indicate a worsening condition and should prompt a medical evaluation.
9.3. Swelling and Inflammation
- Significant swelling and inflammation that do not subside with rest and ice may require medical assessment.
9.4. Loss of Strength
- If you notice a substantial loss of strength in your affected arm, especially during activities you could perform before, it’s time to see a healthcare provider.
9.5. Numbness or Tingling
- Sensations like numbness, tingling, or electric shock-like feelings in the affected arm should not be ignored.
9.6. Difficulty in Daily Activities
- When triceps tendonitis interferes with your ability to perform daily tasks, such as dressing or eating, it’s essential to seek medical advice.
9.7. Fever or Infection
- If you develop a fever or notice signs of infection, such as redness, warmth, or pus around the affected area, seek immediate medical attention.
9.8. Lack of Improvement
- If your symptoms haven’t improved after following conservative treatments and rest as recommended, consult with a healthcare provider for a reassessment.
9.9. Consultation with a Specialist
- In cases where triceps tendonitis becomes chronic or recurrent, consulting with an orthopedic specialist may be necessary for further evaluation and specialized treatment.
9.10. Pain That Interferes with Sleep
- Pain that significantly disrupts your sleep patterns and prevents you from getting restful sleep should prompt a visit to a healthcare professional.
Recognizing these signs and acting promptly by seeking medical attention ensures that triceps tendonitis is adequately assessed and treated, preventing potential complications and promoting a faster recovery.
10. Triceps Tendonitis Recovery Timeline
Understanding the typical recovery timeline for triceps tendonitis can help individuals set realistic expectations regarding their healing process. Here, we provide a general overview of what you can expect during different stages of recovery:
| Stage | Duration | Key Milestones |
| Initial Rest Phase | 2-4 weeks | – Complete rest from aggravating activities |
| – Pain and swelling reduction | ||
| Rehabilitation | 4-6 weeks | – Introduction of gentle exercises |
| – Gradual range of motion improvement | ||
| Progressive Return | 6-12 weeks | – Gradual return to normal activities |
| – Strengthening exercises | ||
| Maintenance | Ongoing | – Continued exercises for tendon health |
| – Monitoring for any symptoms |
Note: The above timeline is a general guideline. Individual recovery times may vary based on factors such as the severity of the condition and adherence to treatment.
10.1. Initial Rest Phase
- During the initial phase, complete rest from activities that worsen the condition is essential.
- Pain and swelling should reduce significantly within the first few weeks.
10.2. Rehabilitation
- Rehabilitation involves the introduction of gentle exercises to improve range of motion.
- The emphasis is on gradual, controlled movements to prevent re-injury.
10.3. Progressive Return
- As symptoms improve, a gradual return to normal activities is possible.
- Strengthening exercises may be introduced to rebuild triceps strength.
10.4. Maintenance
- Even after recovery, it’s essential to continue exercises for tendon health.
- Regular monitoring helps detect any signs of recurrence.
Understanding the stages of triceps tendonitis recovery and the associated timelines allows individuals to gauge their progress and make informed decisions about their activities. Remember that it’s crucial to follow your healthcare provider’s guidance throughout the recovery process.
11. Preventing Triceps Tendonitis Recurrence
Preventing the recurrence of triceps tendonitis is essential to maintain a healthy and pain-free triceps tendon. Here are some strategies to help minimize the risk of triceps tendonitis returning:
11.1. Gradual Return to Activities
- After recovering from triceps tendonitis, avoid rushing back into strenuous activities. Gradually increase the intensity and duration of your exercises and movements.
11.2. Proper Warm-Up and Stretching
- Always warm up before engaging in physical activities, and include stretching exercises to prepare your muscles and tendons.
11.3. Strengthening Exercises
- Incorporate triceps-strengthening exercises into your fitness routine to improve the overall strength of your triceps.
11.4. Maintain Good Posture
- Be mindful of your posture during activities and daily tasks. Good posture reduces the strain on your triceps.
11.5. Hydration and Nutrition
- Stay adequately hydrated to support tendon health. A balanced diet rich in nutrients can also promote tendon health.
11.6. Rest and Recovery
- Ensure that you get enough rest and recovery time between activities to prevent overuse and strain on your triceps.
11.7. Use Proper Technique
- When engaging in sports or exercises, use proper form and technique to avoid unnecessary stress on your triceps.
11.8. Listen to Your Body
- Pay attention to any signs of discomfort or pain in your triceps. If you experience pain, take a break and consult a healthcare provider if needed.
11.9. Brace Usage
- In consultation with your healthcare provider, consider using a triceps tendonitis brace during activities that may pose a risk of recurrence.
11.10. Regular Check-Ins
- Schedule regular check-ups with your healthcare provider to monitor your triceps health and receive guidance on injury prevention.
By implementing these preventive measures and being mindful of your triceps health, you can reduce the risk of triceps tendonitis recurrence and enjoy a more active and pain-free lifestyle.
12. The Role of Ergonomics in Triceps Tendonitis Prevention
Ergonomics plays a significant role in preventing triceps tendonitis, especially for individuals who have jobs or activities that involve repetitive movements. Here, we’ll explore how ergonomic considerations can help reduce the risk of triceps tendonitis:
12.1. Workspace Ergonomics
- Adjustable Workspace: If possible, set up your workspace with adjustable chairs and desks to ensure proper posture during work hours.
- Monitor Placement: Position your computer monitor at eye level to avoid straining your neck and shoulders.
12.2. Proper Seating
- Supportive Chairs: Use chairs that provide adequate lumbar support and cushioning to reduce pressure on the triceps.
12.3. Keyboard and Mouse
- Ergonomic Accessories: Consider using ergonomic keyboards and mice designed to reduce strain on the hands and arms.
- Proper Hand Placement: Maintain a neutral wrist position while typing or using a mouse.
12.4. Lifting Techniques
- Proper Lifting: When lifting objects, use proper lifting techniques to avoid excessive strain on the triceps and other muscles.
- Avoid Overloading: Don’t lift objects that are too heavy for you.
12.5. Driving Ergonomics
- Adjustable Car Seats: If you spend a lot of time driving, ensure your car seat is adjustable to provide proper lumbar support.
12.6. Regular Breaks
- Microbreaks: Take short breaks during work or activities to stretch and relax your triceps and other muscles.
12.7. Sleep Ergonomics
- Mattress and Pillow: Choose a mattress and pillow that provide proper neck and back support to prevent poor sleeping posture.
12.8. Sports and Exercise Equipment
- Proper Equipment: Ensure that sports and exercise equipment fit you well and are suitable for your chosen activities.
12.9. Training and Education
- Workplace Training: Employers should provide ergonomic training to employees to promote healthy work habits.
- Self-Education: Educate yourself about ergonomic principles and apply them in your daily life.
Ergonomic considerations are crucial for preventing triceps tendonitis, especially if your daily activities involve repetitive movements or extended periods of sitting. By making adjustments and practicing good ergonomics, you can reduce the strain on your triceps and other muscles, minimizing the risk of injury.
13. Triceps Tendonitis and Exercise Modifications
Engaging in physical activities is essential for overall health, but individuals with triceps tendonitis may need to modify their exercise routines to prevent aggravating the condition. Here, we’ll discuss exercise modifications for triceps tendonitis:
13.1. Low-Impact Activities
- Swimming: Consider swimming, which is a low-impact exercise that puts minimal strain on the triceps.
- Cycling: Riding a stationary bike or cycling outdoors can be gentle on the triceps.
13.2. Avoid Overhead Exercises
- Overhead Presses: Temporarily avoid exercises like overhead presses, which can strain the triceps.
13.3. Light Resistance
- Light Weights: Use lighter weights during strength training exercises to reduce strain on the triceps.
- Resistance Bands: Incorporate resistance bands, which provide adjustable resistance and can be gentler on the triceps.
13.4. Range of Motion Exercises
- Gentle Stretching: Perform gentle triceps stretches to improve range of motion without overstretching.
- Warm-Up: Prioritize thorough warm-up routines before exercise.
13.5. Listen to Your Body
- Pain Signals: If you experience pain during an exercise, stop immediately and modify or avoid that movement.
13.6. Supervised Rehabilitation
- Physical Therapist: Consider working with a physical therapist who can design a tailored exercise program.
- Progressive Loading: They can guide you through exercises that gradually load the triceps tendon.
13.7. Gradual Progression
- Slow Progress: Progress in your exercise routine gradually, ensuring that your triceps can adapt to increased demands.
13.8. Alternative Exercises
- Switch Exercises: Replace exercises that cause discomfort with alternative movements that work different muscle groups.
- Cross-Training: Explore cross-training options to vary your workouts.
13.9. Focus on Core and Lower Body
- Core Work: Shift your focus to core and lower body exercises while allowing your triceps to heal.
- Maintain Fitness: This allows you to maintain overall fitness during recovery.
Exercise modifications are crucial for individuals with triceps tendonitis to continue enjoying physical activity while minimizing the risk of exacerbating the condition. Always consult with your healthcare provider or physical therapist for personalized exercise recommendations and modifications.
Conclusion
In conclusion, triceps tendonitis is a challenging but manageable condition that can affect individuals of all activity levels. While it can bring discomfort and limitations, it’s reassuring to know that with the right approach, recovery and prevention are possible.
Throughout this comprehensive guide, we’ve explored the various facets of triceps tendonitis, from its causes and symptoms to its diagnosis, treatment options, and prevention strategies. Here are the key takeaways:
- Early Detection Matters: Recognizing the signs of triceps tendonitis, such as pain, swelling, and limited range of motion, allows for early intervention and better outcomes.
- Treatment is Multifaceted: The treatment of triceps tendonitis involves a combination of rest, physical therapy, pain management, and, in some cases, medical interventions. It’s essential to follow your healthcare provider’s recommendations.
- Rehabilitation is Key: Rehabilitation plays a crucial role in recovery, helping individuals regain strength, flexibility, and function in their triceps.
- Prevention is Possible: By adopting ergonomic practices, modifying exercise routines, and practicing good self-care, you can significantly reduce the risk of triceps tendonitis or its recurrence.
- Consult a Professional: If you suspect or are diagnosed with triceps tendonitis, seek guidance from a healthcare provider or physical therapist. They can provide tailored advice and treatments to suit your specific needs.
Remember that everyone’s journey with triceps tendonitis is unique. It may take time and patience, but with dedication to your treatment plan and preventive measures, you can overcome this condition and continue to lead an active, pain-free life.
Your triceps are essential for numerous daily activities and sports, and taking care of them is an investment in your long-term well-being. Stay proactive in managing your triceps health, and don’t hesitate to reach out to healthcare professionals for support and guidance on your path to recovery and prevention.
If you have any more questions or seek further information on triceps tendonitis, please feel free to explore the FAQs below or consult with a medical expert for personalized advice.
FAQ’s
1. What is triceps tendonitis, and what causes it?
Triceps tendonitis is the inflammation of the triceps tendon, a thick cord-like structure connecting the triceps muscle to the back of the elbow. It is often caused by overuse, repetitive motions, or sudden increases in physical activity. Activities like weightlifting, sports, or jobs that involve repetitive arm movements can contribute to its development.
2. What are the common symptoms of triceps tendonitis?
Common symptoms of triceps tendonitis include:
- Pain at the back of the upper arm near the elbow
- Swelling and tenderness in the affected area
- Limited range of motion in the elbow joint
- Weakness in the triceps muscle
3. How is triceps tendonitis diagnosed?
Triceps tendonitis is typically diagnosed through a combination of methods, including:
- Physical Examination: A healthcare provider assesses the affected area for pain, tenderness, and range of motion.
- Medical History: Discussing your symptoms and activities helps in the diagnostic process.
- Imaging Tests: Ultrasound or MRI scans may be used to visualize the extent of tendon damage or inflammation.
4. What are the treatment options for triceps tendonitis?
Treatment for triceps tendonitis may involve:
- Rest: Giving the affected tendon time to heal.
- Physical Therapy: Exercises and stretches to improve flexibility and strength.
- Anti-Inflammatory Medication: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) to reduce pain and swelling.
- Corticosteroid Injections: In severe cases, corticosteroid injections can provide relief.
- Surgery: Rarely, surgery may be needed for severe or chronic cases to repair the tendon.
5. Can I continue exercising with triceps tendonitis?
Exercise can be beneficial during triceps tendonitis recovery, but it’s crucial to modify your exercise routine to avoid aggravating the condition. Consult with a healthcare provider or physical therapist to ensure safe and appropriate exercises that won’t strain the triceps tendon.
6. How long does it take to recover from triceps tendonitis?
Recovery times vary depending on the severity of the condition and individual factors. With proper treatment and adherence to rehabilitation exercises, most individuals can expect improvement within a few weeks to a few months.
7. Are there any preventive measures for triceps tendonitis?
Yes, preventive measures include:
- Maintaining good ergonomics in your daily activities.
- Gradually progressing in exercise routines to avoid overuse.
- Proper warm-up and stretching before physical activity.
- Listening to your body and recognizing when to rest and recover.
8. Can triceps tendonitis recur after recovery?
Yes, triceps tendonitis can recur, especially if preventive measures are not followed. However, by maintaining good triceps health practices, including proper warm-up, exercise modifications, and listening to your body, you can significantly reduce the risk of recurrence.
9. What are some triceps-strengthening exercises for rehabilitation?
Rehabilitation exercises may include:
- Gentle triceps stretches to improve range of motion.
- Light resistance training using bands or weights to strengthen the triceps.
- Gradual reintroduction of overhead movements while closely monitoring pain and discomfort.
10. When should I seek medical attention for triceps tendonitis?
Seek medical attention if you experience:
- Severe pain that limits your daily activities.
- Persistent symptoms that don’t improve with rest.
- Significant weakness in the triceps muscle.
- Any other concerns about your triceps health.
Remember, early intervention and professional guidance are key to managing triceps tendonitis effectively.